State & Federal
Louisiana

Timeline
1901 — The antebellum plantation property Angola which was later used by former Confederate Major Samuel Lawrence Jones to run a convict leasing system, is converted into Louisiana State Penitentiary. The Louisiana State Penitentiary is now used to house male death row prisoners.
1946 — At 17, Wille Francis survives a botched execution by electric chair. After his appeal failed in the U.S. Supreme Court, Mr. Francis was returned to the electric chair in 1947 and executed.
1990 — Dalton Prejean is executed in Louisiana by the electric chair for a crime he committed at age 17. Mr. Prejean was convicted by an all-white jury and had brain damage, with an IQ of 71.
2001 — Michael Ray Graham Jr. and Albert Ronnie Burrell are exonerated from death row after serious prosecutorial misconduct and the testimony of a jailhouse snitch led to their wrongful convictions.
2008 — In Kennedy v. Louisiana, the U.S. Supreme Court strikes down an unconstitutional state-statute that allowed death sentencing for the rape of a child, where the victim did not die.
2010 — The Louisiana Department of Public Safety and Corrections sues every inmate on Louisiana’s death row in an effort to block them from challenging the state’s lethal injection procedures.
2012 — Damon Thibodeaux is freed from Louisiana’s death row after 15 years at Angola once new DNA evidence was tested.
2013 — A federal magistrate rules that the Louisiana Department of Safety and Corrections must reveal the details of the state’s lethal injection protocol.
2014 — One week in advance of a scheduled execution, Louisiana obtains hydrocodone from a pharmacy at Lake Charles Memorial Hospital after falsely claiming the medication was needed for a “medical patient.” Hydrocodone is one of the drugs used in Louisiana’s lethal-injection protocol.
2015 — A Louisiana federal judge delays five executions until 2016, following state officials’ struggle to determine how to conduct executions using lethal injection. The Department of Safety and Corrections’ supply of lethal injection drugs has now expired.
2016 — Louisiana delays executions until 2018 after a new court order issued with the consent of the parties in federal proceedings challenges the constitutionality of Louisiana’s lethal injection process. Louisiana’s protocol allows for either a one-drug execution using pentobarbital, or a two-drug execution procedure using midazolam and hydromorphone, but the state does not have the drugs necessary for either option.
2017 — Rodricus Crawford is exonerated from Louisiana’s death row amid evidence of racial discrimination, prosecutorial overcharging, and his innocence.
2018 — A Louisiana federal court judge orders another years of stayed executions to allow the proceedings to continue in the death row prisoners’ challenge to the state’s lethal injection protocol.
2023 — The Louisiana Board of Pardons and Parole sets aside all 56 clemency applications filed by nearly every death-sentenced prisoner in Louisiana without reviewing the merits of any of them. The petitions raise claims of severe mental illness, racial injustice, intellectual disability, prosecutorial misconduct, among many others.
Famous Cases
Connick v. Thompson, 563 U.S. 51 (2011)
John Thompson was convicted of robbery and murder, and spent 18 years in prison, 14 of which were spent on death row, before being exonerated. Shortly before Thompson’s scheduled execution, an investigator discovered that prosecutors had hidden blood evidence that exonerated Thompson.
Mr. Thompson sued the Orleans Parish District Attorney’s Office, the District Attorney, Harry Connick, in his official and individual capacities, and several assistant district attorneys in their official capacities under 42 U.S.C § 1983 in a Louisiana federal district court. The jury awarded Mr. Thompson $14 million against Mr. Connick in his official capacity.
In a 5 – 4 decision, the US Supreme Court held that a prosecutor’s office could not be held liable for the illegal conduct of one of its prosecutors when there has been only one violation resulting from that deficient training. In dissent Justices Ginsburg, Breyer, Sotomayor and Kagan argued that the evidence “established persistent, deliberately indifferent conduct for which the District Attorney’s Office bears responsibility under §1983.”
Kennedy v. Louisiana, 554 US 407 (2008)
Kennedy v. Louisiana barred the death penalty from being used in non-homicide offenses. In a 5 – 4 decision the Court held that the Eighth Amendment bars states from imposing the death penalty for the rape of a child where the crime did not result in the child’s death. The majority opinion found that applying the death penalty in such a case would be an exercise of “cruel and unusual punishment” in violation of a national consensus on the issue.
Roberts v. Louisiana, 428 U.S. 325 (1976)
Stanislaus Roberts v. Louisiana was one of the five death penalty cases the Supreme Court decided on July 2, 1976 when it ruled in Gregg v. Georgia that the death penalty did not invariably constitute cruel and unusual punishment. However, in a 5 – 4 vote, the Court declared that Louisiana’s capital punishment statute, which made the death penalty mandatory for certain murders was unconstitutional because it did not allow for consideration of mitigating factors or the exercise of mercy to spare a defendant’s life. The Supreme Court took up another Louisiana case in 1977 to determine whether a mandatory death sentence could be imposed in the limited circumstance of the murder of a law enforcement officer during the performance of his or her official duties. In a 5 – 4 decision in Harry Roberts v. Louisiana, 431 U.S. 633 (1977), the Court held that the prohibition against mandatory death sentences encompassed murders of police officers.
Notable Exonerations
Curtis Kyles was convicted and sentenced to death in 1984 after his first trial ended in a hung jury. The U.S. Supreme Court reversed his conviction in the case Kyles v. Whitley, 514 U.S. 419 (1995). The Court cited prosecutorial misconduct: the state had withheld crucial information about a paid informant who may have been the actual murderer. He was retried three times, but each jury deadlocked. After Kyles’ fifth trial, prosecutors dropped the charges against him. He was released from prison in 1998.
Other Interesting Facts
Intellectual disability (formerly known as mental retardation) is determined by the jury in the penalty phase of a capital trial following conviction for first-degree murder: http://www.legis.state.la.us/lss/lss.asp?doc=191015
Sister Helen Prejean began her work against the death penalty in Louisiana when she visited Patrick Sonnier on Death Row at Angola and accompanied him to his execution. Her account is documented in the book and movie Dead Man Walking.
Resources
- Louisiana Coalition for Alternatives to the Death Penalty
- Capital Post Conviction Project of Louisiana – Provides indigent capital defendants with representation in state post-conviction and federal habeas corpus
- Capital Appeals Project – Provides indigent capital defendants with representation on direct appeal
- Louisiana Capital Assistance Center – A resource center for indigent capital defense at the trial level
- Department of Corrections
- Prosecutors
- Victims’ services
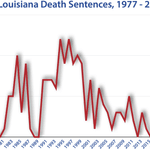
Louisiana Execution Totals Since 1976
News & Developments
News
Sep 08, 2025
DPI Analysis: Death Warrants Under a Spotlight
40 active death warrants have been issued in the United States thus far in 2025 — more than a third of them were issued by one individual, Florida Governor Ron DeSantis, in a process cloaked in secrecy. The only two states that place authority solely in the hands of the governor to issue an execution warrant are Florida, which has executed more individuals in 2025 than any other state, and Pennsylvania, which has not executed anyone in over 25 years and where a…
Read MoreNews
Jul 14, 2025
New Louisiana Legislation Will Limit Post-Conviction Appeals, Endangering Innocent Prisoners in an Attempt to Expedite Executions
Recent legislation signed by Louisiana Governor Jeff Landry drastically restricts the ability of prisoners to challenge their convictions, which those opposed to the law have argued could lead to the execution of innocent prisoners. HB 675, signed into law in June 2025, imposes strict time limits on post-conviction relief applications and introduces“abandonment” rules that cut off appeal options for prisoners who fail to meet the law’s strict deadlines. The…
Read MoreNews
Jul 08, 2025
ACLU Report Shows How Death Penalty Jury Selection Discriminates Against Black Americans, Women, and People of Faith
A new report from the ACLU documents how the process of selecting juries for death penalty cases systematically excludes Black prospective jurors, women, and people of faith, fundamentally undermining the constitutional promise of a trial by a jury of one’s peers. The report, Fatal Flaws: Revealing the Racial and Religious Gerrymandering of the Capital Jury, examines the practice of“death qualification,” a requirement that potential jurors must be…
Read MoreNews
Jun 04, 2025
2025 Roundup of Death Penalty Related Legislation
More than one hundred bills have been introduced this year in 34 states and in Congress to expand and limit use of the death penalty, abolish and reinstate the death penalty, modify execution protocols and secret the information about them, and alter aspects of capital trials. Thus far, nine bills in five states have been enacted, with Florida enacting the most legislation. Of the bills that have been signed into law, three modify execution protocols; two expand…
Read MoreNews
Apr 28, 2025
Louisiana Judge Sets Aside Jimmie Duncan’s Conviction and Death Sentence Based on “No Longer Valid” Bite Mark Evidence
On April 24, 2025, Louisiana District Court Judge Alvin Sharp set aside Jimmie Duncan’s first-degree murder conviction and death sentence. Mr. Duncan was sentenced to death for the 1993 death of his girlfriend’s toddler largely based on faulty bite mark evidence. Judge Sharp, in a decision that came after a September 2024 evidentiary hearing, held that expert testimony presented during this hearing demonstrated the bite mark analysis used against Mr. Duncan is“no…
Read More